Dry Days / No Alcohol Days in Delhi Delhi is a bustling metropolis with a vibrant culture and a diverse population. However, there are certain days of the year when the city observes dry days, during which the sale and consumption of alcohol are prohibited. These dry days are typically observed on important national and […]
Main Content
Information

Delhi Premium Buses: Book Online through App Only
Delhi’s App-Based Premium Buses Seat reservations are now set to take place prior to departure as the path is paved for the implementation of the Premium Bus Aggregator Scheme in Delhi, following the issuance of a notification. Similar to how residents of Delhi-NCR currently book cabs, autos, or bike taxis via mobile apps, the ability […]

Royal Enfield Himalayan 450: Price and Technical Specifications
Himalayan 450 In the realm of adventure motorcycles, the Royal Enfield Himalayan 450 stands out as a capable and versatile machine, designed to tackle diverse terrains and conquer adventurous journeys. This robust motorcycle, an evolution of its predecessor, the Himalayan 411, boasts a refined engine, enhanced performance, and a range of features that make it […]
News
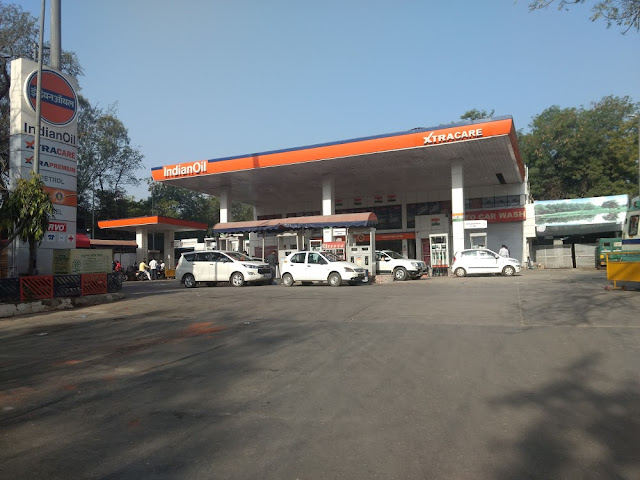

Strict Enforcement from July 1: No Fuel for 15-Year Petrol, 10-Year Diesel Vehicles in Delhi
As part of Delhi’s long term goal of combating air pollution and enforce environmental regulations Delhi’s government is making all necessary steps to enforce the ban on refuelling end-of-life vehicles. What are End-of-Life Vehicles? These are the vehicles which have crossed their legal age of limit including Petrol vehicles that are more than 15 years […]
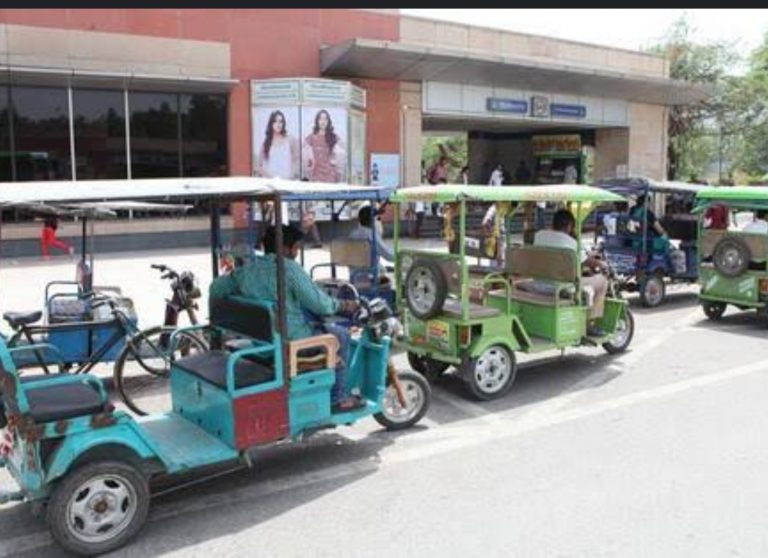

Why Delhi Transportation Department is Crushing Hundreds of E-Rickshaws
In parts of Delhi, excavators are crushing e-rickshaws into scrap. These vehicles, once a lifeline for commuters, are being destroyed by the hundreds. This move aims to address the on-going traffic problems in the city. So far, the Transport Department has destroyed 566 illegal e-rickshaws, with many more expected to be crushed soon. Owners of […]
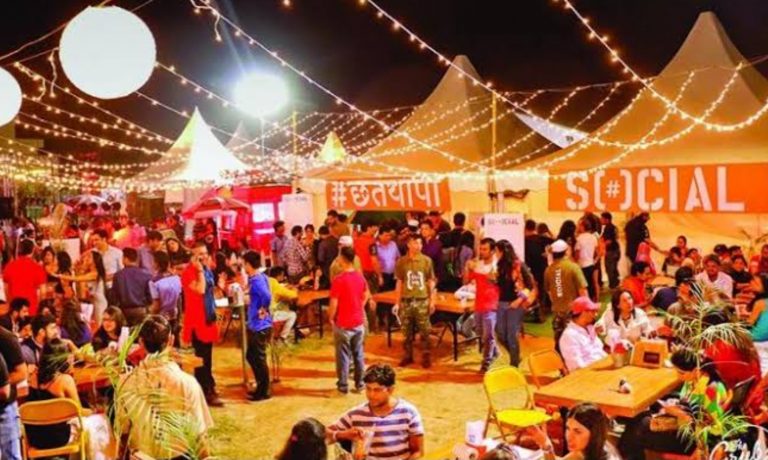

Burrp Fest 2024: Delhi’s Biggest Beer Festival
Get Ready, Delhi! Burrp Fest is Back for a Weekend of Beer and Good Times! Have you been dreaming of a proper beer festival all summer? Well, Burrp Fest heard you! Scheduled from September 6 to September 8, 2024, this festival promises to be a delightful celebration for beer lovers and food enthusiasts alike. Set […]
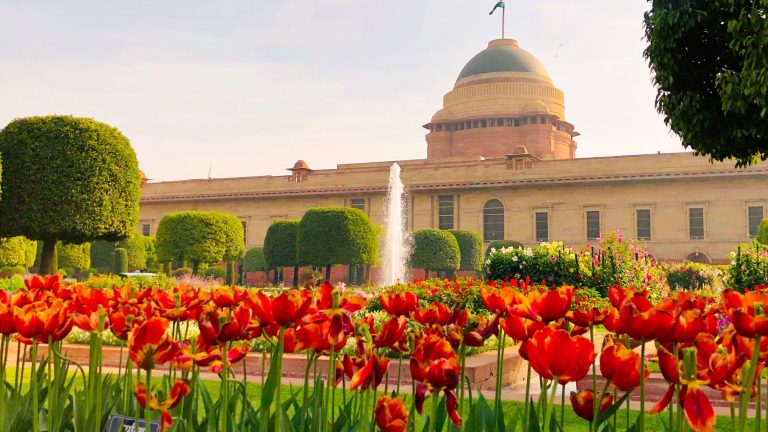

Amrit Udyan Welcomes Visitors for Summer Bloom Display
Delhi is ready for a burst of summer colors! Amrit Udyan, formerly known as Mughal Gardens, at Delhi’s Rashtrapati Bhavan is reopening to the public on August 16. This reopening is part of the second phase of the Udyan Utsav, which was announced earlier this year. Spread over 15 acres, Amrit Udyan is set to […]
Delhi Travel
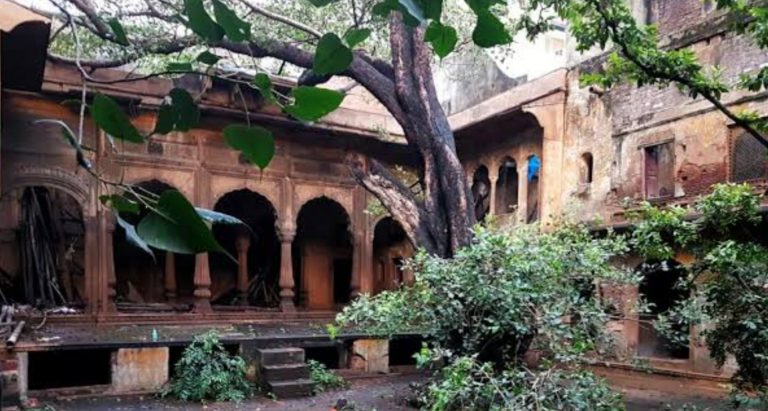

Delhi’s Decaying Buildings Getting a New Lease on Life
Delhi, a city steeped in rich history and architectural marvels, has a large number of old, abandoned buildings. As it grapples with the issues of increasing population, the reuse of these rundown sites has often entailed demolition and new construction, generating waste and contributing to environmental concerns. However, in recent years, Delhi and many other […]
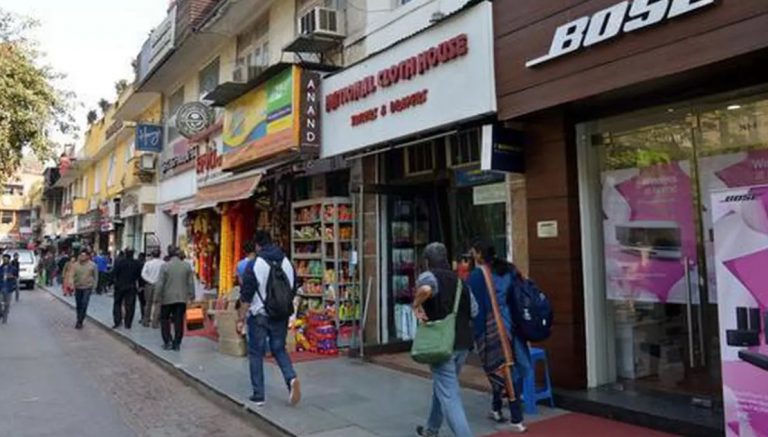

Unveiling Khan Market: Delhi’s Chic Shopping Paradise
Delhi, India’s vibrant capital, is a captivating blend of ancient and modern. Here, towering skyscrapers share the skyline with historic monuments, and traditional bazaars coexist with upscale shopping malls. Today, let’s explore one of Delhi’s most iconic shopping destinations - Khan Market. Khan Market: From Humble Beginnings to Upscale Haven Named after Indian freedom fighter […]

Sarai Rohilla Railway Station (DEE)
Delhi Sarai Rohilla Railway Station The Delhi Sarai Rohilla railway station (station code: DEE) is a major railway station in the Indian city of Delhi. It is situated about 4 kilometers (2.5 mi) from Old Delhi railway junction. The station is managed by the Delhi Division of Northern Railway zone. Many trains from Delhi to […]
Delhi Locations

Azadpur Sabzi Mandi: The Largest Fruit and Vegetable Market in Asia
Azadpur Sabzi Mandi Nestled in the heart of Delhi, Azadpur Sabzi Mandi stands as a bustling testament to India’s agricultural prowess. This sprawling wholesale market, often referred to as the ‘lifeline of fresh produce,’ plays a vital role in connecting farmers from across the country with consumers in one of India’s largest metropolitan areas. With […]

Japanese Park Delhi: Pictures, Operating Hours, Boating, and Lush Green Landscapes
Japanese Park Delhi Nestled within the vibrant heart of Delhi, Swarn Jayanti Park, commonly known as the Japanese Park Delhi, stands as an idyllic sanctuary where the grace of Japanese aesthetics merges seamlessly with the rich tapestry of Indian culture. This verdant oasis, with its luxuriant gardens, peaceful ponds, and painstakingly designed structures, provides a […]

Museum of Illusions New Delhi Tickets: Everything You Need to Know
If you’re looking for a unique and mind-bending experience in New Delhi, the Museum of Illusions is the perfect destination. With many exhibits that challenge your perceptions and trick your senses, this museum is unlike any other. Here’s everything you need to know about Museum of Illusions New Delhi tickets. Here you can have fun […]
Weather

Delhi’s Weather Whirlwind: Rain Alert Sparks December Dilemma!
Get ready for a meteorological rollercoaster in Delhi! The Meteorological Department just unleashed a rain alert, and the drama could linger until December. Cloudy skies, a hint of rain, and a foggy mystery. What’s Brewing in Delhi’s Skies? The weather wizards at the Meteorological Department have thrown a curveball – a rain alert that might […]

Delhi Rain Alert: Scorching Sun in Delhi, Know when will it Rain in Delhi
Delhi Weather Update After the respite due to rains in Delhi, people are again facing scorching heat. The standard observatory Safdarjung recorded a maximum temperature of 40.5 degrees Celsius on Friday, which was one degree above normal. While the minimum temperature was 27.3 degree Celsius. At the same time, in many areas the temperature crossed […]
Delhi Metro
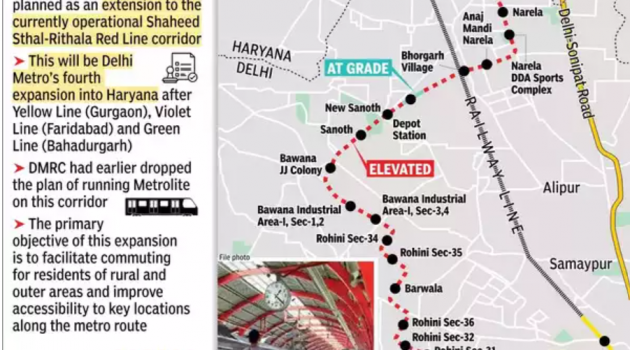
Delhi Metro Phase IV Corridor - Rithala - Narela - Kundli - Nathupur
Image Source: Times of India The existing corridor of Delhi Metro’s Rithala - Narela will be extended to the inside of Kundli-Nathupur in Haryana as announced by transport minister Kailash Gahlot. Delhi government has given an in-principle approval to the extension and will send the proposal to the central government to enable tendering to start […]

Delhi Metro Phase IV Progress, Priority Corridors, Line, Route, Stations
Janakpuri West to Krishna Park Extension By August end, commuters in Delhi can expect the functioning of 2.5-km section from Janakpuri West to Krishna Park Extension on the Janakpuri West-RK Ashram Marg Metro corridor of Phase-IV. This will be the first section to open in Delhi Metro Phase IV – said commissioner of Delhi Metro […]
